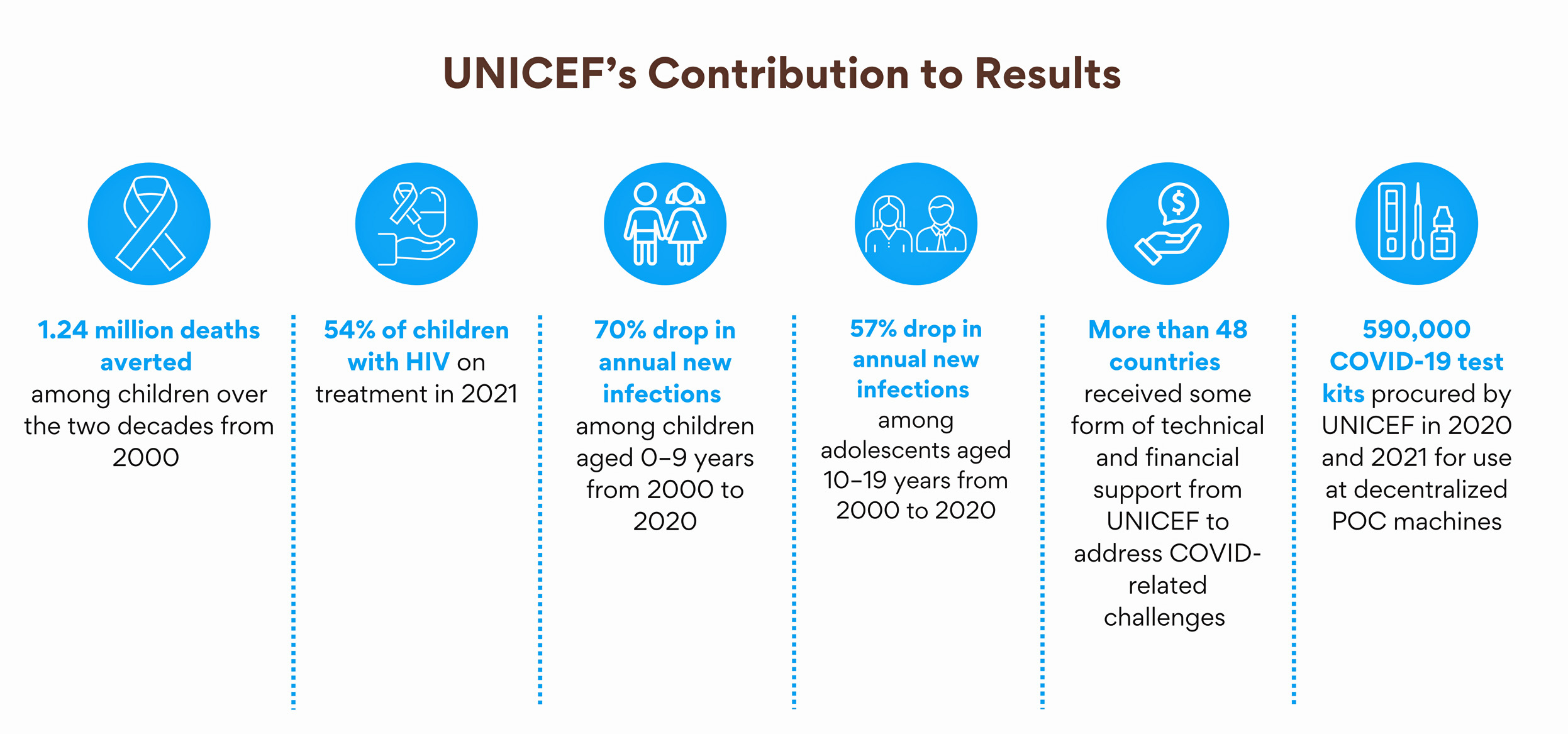
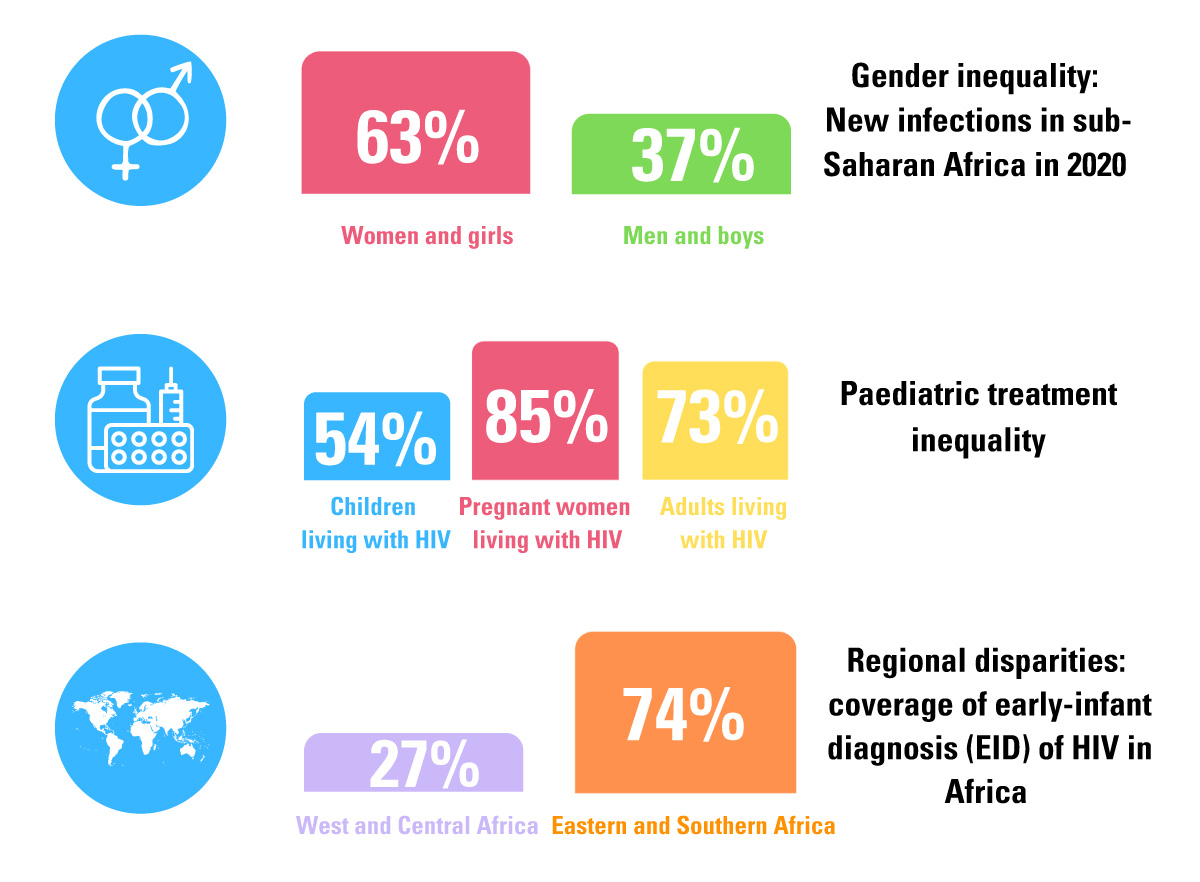
The Global Alliance to end AIDS in Children Framework
An end to AIDS in children, achieved through a strong, strategic, and action-oriented alliance of multisectoral stakeholders at national, regional, and global levels that works with women children and adolescents living with HIV, national governments, and partners to mobilize leadership, funding, and action to end AIDS in children by 2030.